Applied Statistics Assignment Help | Sample Question Paper
- realcode4you
- Jan 20, 2023
- 4 min read
Part 1
Use below table to answer the given below questions.

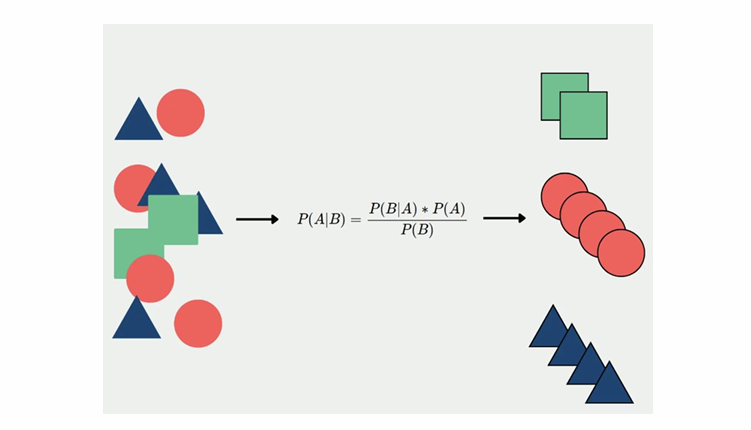
Q 1. A Use above table to find the joint probability of the people who planned to purchase and actually placed and order.
Q 1. B Use above table to find the joint probability of the people who planned to purchase and actually placed and order, given that people planned to purchase.
Q 2. An electrical manufacturing company conducts quality checks at specified periods on the products it manufactures. Historically, the failure rate for the manufacturing item is 5%. Suppose a random sample of 10 manufactured items is selected. Answer the following questions.
A. Probability that none of the items are defective?
B. Probability that exactly one of the items is defective?
C. Probability that two or fewer of the items are defective?
D. Probability that three or more of the items are defective?
Q3. A car salesman sells on an average 3 cars per week.
A. What is probability that in a given week he will sell some cars.
B. What is probability that in a given week he will sell 2 or more but less that 5 cars.
C. Plot the Poisson distribution function for cumulative probability of cars sold per-week ns number of cars sold per week.
Q4. Accuracy in understanding orders for a speech based bot at a restaurant is important for the Company X which has designed, marketed and launched the product for a contactless delivery due to the COVID-19 pandemic. Recognition accuracy that measures the percentage of orders that are taken correctly is 86.8%. Suppose that you place an order with the bot and two friends of your independently place orders with the same bot. Answer the following questions.
A. What is the probability that all three orders will be recognised correctly.
B. What is the probability that none of the three orders will be recognised correctly.
C. What is the probability that at least two of the three orders will be recognised correctly?
Q5. Explain 1 real life industry scenario(other than the ones mentioned above) where you can use the concepts learnt in this module of Applied statistics to get a data driven business solution.
Code Implementation
# importing libraries
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import warnings
import matplotlib.animation as animation
import seaborn as sns
import math
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
sns.set(style="darkgrid")
pd.set_option('display.max_columns', 100)
pd.set_option('display.max_colwidth', -1) # data and columns are displayed correctly
pd.options.display.float_format = '{:20,.2f}'.format # display float value with correct precision
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')## Que1a
##You observe from the above table, that 400 people planned to purchase and actually placed an order is
##400 out of 2000 people.
plan_purchase = 400
total = 2000
joint_prob = round(plan_purchase/total,4)
joint_probOutput:
0.2
##Que1b
# P1 = P(Actually placed an order | Planned to purchase)
# P2 = Planned to purchase and actually placed an order
# P3 = Planned to purchase
## P1 = P2/P3
P1 = (400 / 2000 )/ (500 / 2000)## Que2
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import scipy.stats as stats
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
p = 0.05 # failure rate of products that the company manufactures is 5%
n = 10 # sample size
k = np.arange(0,11) # An array of quantiles
binomial = stats.binom.pmf(k,n,p)
print(binomial)Output:
[5.98736939e-01 3.15124705e-01 7.46347985e-02 1.04750594e-02 9.64808106e-04 6.09352488e-05 2.67259863e-06 8.03789063e-08 1.58642578e-09 1.85546875e-11 9.76562500e-14]
## que2a
binomial[0]Output:
0.5987369392383789
## que2b
binomial[1]Output:
0.31512470486230504
## que2c
cumbinomial = stats.binom.cdf(k,n,p)
cumbinomial[2]Output:
0.9884964426207031
## que2d
P = 1- cumbinomial[2]
POutput:
0.01150355737929687
## Que3
rate = 3 # which is the mean
n = np.arange(0,16)
cumpoisson = stats.poisson.cdf(n,rate)
cumpoissonOutput:
array([0.04978707, 0.19914827, 0.42319008, 0.64723189, 0.81526324, 0.91608206, 0.96649146, 0.9880955 , 0.99619701, 0.99889751, 0.99970766, 0.99992861, 0.99998385, 0.9999966 , 0.99999933, 0.99999988])
## que3a
P = 1 - cumpoisson[0]
POutput:
0.950212931632136
## que3b
# Let P1 be the probability that the salesman sells more than 4 cars
P1 = cumpoisson[4] # P(X >=4)
# Let P2 be the probability that the salesman sells more than 1 cars
P2 = cumpoisson[1] # P(X >=1)
P = P1 - P2 # Prob. that the salesman will sell between 2 and 5 cars
POutput:
0.6161149710523164
## que3c
poisson = stats.poisson.pmf(n,rate)
plt.plot(n,poisson, 'o-')
plt.title('Poisson')
plt.xlabel('Number of cars sold per week')
plt.ylabel('Cumulative Prob of cars sold per week')
plt.show()Output:

## Que4
#Because there are three orders and the probability of a correct order is 0.868.
# Using Binomial distribution equation,
P(X = 3|n =3, pi given = 0.868)
3!/ 3!(3-3)! * (0.868)^3 * (1-0.868)^3-3 = 0.6540
Likewise, calculate X= 0, X=2
(X = 0) = 0.0023
(X = 2) = 0.2984
Hence, P(X>=2) = P(X=2)+P(X=3) = 0.9524
## que4a - The probability that all the three orders are recognized correctly is 0.6540, 65.4% .
## que4b - The probability that none of the orders are recognized correctly is 0.0023, 0.23% .
## que4c - The probability that atleat two of the three are recognized correctly is 0.9524, 95.24%## Que5
Insurance firms employ the theory of probability or theoretical probability when developing a policy or determining a premium rate. Probability theory is a statistical strategy for predicting the potential of future outcomes. For example, Issuing health insurance to an alcoholic is likely to be more expensive than giving health insurance to a healthy individual. Statistical study reveals that a habitual drinker faces substantial health risks, posing a significant financial risk due to the increased likelihood of severe sickness and, as a result, the need to file a claim for premium money.We are also providing statistics assignment help, homework help and project help. If you need any help in applied statistics assignments and projects then you can send your requirement details at:
realcode4you@gmail.com


Are your assignments piling up? Worried you won’t meet your deadlines? Feeling overwhelmed by your coursework?
You’re not alone—and our assignment help is just a message away.
At Get Assignment Help Australia, we offer 100% AI-free, custom-written academic support crafted by native Australian assignment writers. Our expert team ensures your work is completed on time, with the quality and attention your education deserves.
Quick Links:
MBA Assignment Help
Nursing Assignment Help
Law Assignment Help
Finance Assignment Help
Marketing Assignment Help
Economics Assignment Help
Computer Engineering Assignment Help
Dissertation Help
Research Paper Writing Services
Case Study Assignment Help
Thesis Writing Help
Assignment Samples
This article provides a practical sample question paper for applied statistics, making it highly beneficial for students seeking to improve their understanding of the subject. For those needing additional support, leveraging statistics assignment help services can further enhance problem-solving skills and ensure clarity on complex concepts.
This resource is a valuable asset for students studying statistics. It provides clear explanations and helpful examples. For those seeking additional support, I recommend considering the services offered by The Programming Assignment Help. We provide comprehensive assistance and timely delivery.
Seeking help with statistics assignments provides students with expert guidance to navigate complex statistical concepts and problems. This support includes assistance with data analysis, hypothesis testing, regression models, and using statistical software. Skilled tutors offer personalized sessions to clarify difficult topics, ensure accurate interpretation of results, and help with assignments and projects. By leveraging their expertise, students can improve their understanding of statistics, complete assignments on time, and achieve better grades. Statistics assignment help also aids in developing analytical skills and applying statistical methods effectively in real-world scenarios.