ER Diagram Assignment Help UK, India, Australia, Canada etc. From Native Experts | Realcode4you
- realcode4you
- Apr 30, 2025
- 4 min read
What is ER Diagram?
The original E-R model is drawn using:
- Rectangles for entities
- Diamonds for relationship
- Connected ellipses for attribute

Variations of the E-R Model
- At least three different versions of E-R model are in use today.
Information Engineering (IE) Crow’s Foot model
Integrated Definition 1, Extended (IDE1X)
Unified Modeling Language (UML)
E-R Diagram – IDEF1X
- IDEF1X standard E-R modeling incorporates the basic ideas of the E-R model but uses different graphical symbols.
- IDEF1X is complex and unwieldy and is not very popular.
- IDEF1X is a national standard but it is very difficult to understand and use.

E-R Diagram – UML
- To add further complications, a newer object-oriented development methodology is introduced called Unified Modeling Language (UML).
- UML adopted E-R model but introduced its own symbols while adding an object-oriented programming spin on it.
- It is beginning to see widespread use among Objected-oriented practitioners.


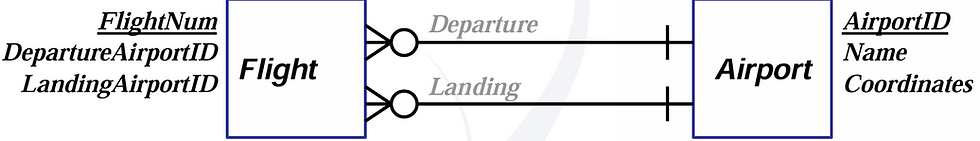
E-R Diagram – IE Crow’s Foot
Crow’s Foot modeling uses slightly different symbols for showing the relationships (both maximum and minimum cardinalities) between entities:
- Instead of a diamond box for specifying maximum cardinality relationship, it use a
( | ) symbol (vertical hash mark) for 1 relationship and a ( < ) crow’s foot for many
relationship.
- For minimum cardinality, O (circle) symbol is used for optional relationship and ( |
) symbol (vertical hash mark) is used for mandatory relationship.
- Symbols that are next (closer) to the entities are used for maximum cardinality.

Crow’s Foot modeling Symbols


E-R Diagram – Strong / Weak Entity
Strong Entity:
- An entity that represents something that can exist on its own.
- Example: PERSON, AUTOMOBILE, BUILDING
- Strong entities are called Non ID-Dependent entities.
Weak Entity:
- An entity whose existence depends on the presence of another entity.
- Example: APARTMENT depends on existence of BUILDING
- Part of the primary key for a weak entity is borrowed from the primary key of the
strong entity.
- Weak entities are called ID-Dependent entities.
- So, ID-dependent entity is a weak entity whose identifier includes the identifier of
another entity.
Relationship between a Strong Entity and a Strong Entity:
- A relationship between two strong entities is a strong relationship.
- Strong relationships are also called non identifying relationships.
- Strong relationships are drawn using dashed (----) line between the entities.

Relationship between a Strong Entity and a Weak Entity:
- A relationship between a strong entity and a weak entity is a weak relationship.
- Weak relationships are called identifying relationship.
- Because weak entity carries the identifier (primary key) from the strong entity, in a weak relationship, strong entity is always considered as a parent entity and the weak entity is considered as a child entity.
- Weak relationship is drawn using a solid line between the entities.
- In this examples, PHONE is a weak entity with part of the identifier is a primary key of the entity, COMPANY.

Super-type & Subtype Entities:
- Another type of weak entity is a subtype entity.
- A subtype is a sub-grouping of the entities in an entity type that shares common attributes or relationships distinct from other subgroups.
- Subtypes inherit all super-type attributes.
- Super-type is an entity type that has a parent/child relationship with one or more subtypes with attributes that are shared with its subtypes.
- Super-types are parents entities while sub-types are considered as child entities.
There are two types of Sub-types entities:
- Exclusive Sub-types: one super-type relates to at most one sub type. Exclusive
subtypes are drawn using a circle with filled in X.
- Inclusive Sub-types: one super-type can relates to one or more sub-types.
Inclusive subtypes are drawn using open circle.
- All sub-type entities have the same identifier (primary key) as their super-type
entity.
- Relationships connecting super-type and sub-types are weak relationship.
- Thus, super-type entity is the parent entity and subtype entities are considered
children


E-R Diagram - Relationships

Crow’s Foot E-R Data Model

E-R Diagram – Best Practices
Entity Rules:
- Every entity table must have attribute(s). If you do not have any attribute, you do not need an entity with just PK.
- You cannot have a stand-alone entity in a database. Every entity table must be connected to at least one other table.
- Do not include foreign key in your E-R model.
- You cannot have the same PK as another entity’s PK unless it is a supertype/subtype relationship.
- When Composite PK borrowed from another entity. The entity must be a weak entity. Alternatively, you can use a Surrogate key to keep it as a strong entity.
Relationship Rules:
- A relationship between two strong entities must be strong.
- A relationship between a strong entity and a weak entity must be a weak relationship.
- Avoid having circular relationships. If you have a circular relationship between a, b, and c, you should be able to remove one of the three relationships and still be able to access each other information.
- Avoid having M-M relationships. Why do you need them?
- Minimum cardinality for the one side cannot be optional while many side is mandatory. Always make many side optional.
- If they have 1:1 relationship with same PK in the both table, why do you need two tables? You might as well place all attributes in one.
Super-type & Subtype Entities Rules:
- Subtypes must be weak entities.
- You must have at least two subtypes to create supertype/subtype relationships.
- Each subtype entity must have a PK that is same as the PK of the supertype.
- Supertype/Subtype relationships must be specific (inclusive or exclusive).
- Cardinalities are not needed for Supertype/Subtype relationships.
- Avoid having relationship with subtype entities. Instead, the relationship should be with their supertype.
- If attributes for each subtypes are same, there is no need for the subtypes. The rule is all subtypes must have different set of attributes.


I’ve had a very positive experience with Zentra Orthopedic Shoes. As soon as I started wearing them, I could feel the difference in comfort and support. The cushioning is soft but still supportive, which makes them great for long days on my feet. They fit comfortably, feel well made, and the materials are clearly durable. Even after regular wear, the shoes still maintain their shape and support.
As a customer, my experience with Twill Tees has been extremely positive. From the moment I started wearing them, I noticed the superior comfort and excellent orthopedic support they provide. The cushioning feels soft yet supportive, making them ideal for long hours of walking or standing. The fit is comfortable and well-structured, and the materials feel high-quality and durable. Even after regular use, the shoes maintain their shape and support without wearing down.
I Organized my Umrah through a reputable UK-based Islamic Tour Agency, and the overall experience exceeded my expectations. From the initial consultation to the completion of the journey, everything was managed professionally with close attention to detail, ensuring a smooth and stress-free process. The ATOL-protected services provided complete peace of mind, while the knowledgeable team guided us clearly through every stage of the visa application. Our stay in Makkah was excellent, featuring accommodation in a clean and luxurious 5-star hotel located just a short walking distance from the Haram, allowing us to perform Umrah comfortably and with full spiritual focus. The entire journey was well-organized, peaceful, and deeply fulfilling. For anyone seeking a reliable and experienced UK-based Islamic Tour Agency…
I booked my Umrah through a UK-based travel agency offering an excellent Umrah Tour Package UK, and the experience surpassed all expectations. From the outset, everything was managed with great professionalism and attention to detail, ensuring a smooth and stress-free journey. The ATOL-protected services gave us complete peace of mind, and the team provided clear, step-by-step guidance throughout the visa process. Our stay in Makkah was outstanding. We were accommodated in a clean and luxurious 5-star hotel located just a few minutes from the Haram, making the performance of Umrah incredibly convenient and spiritually fulfilling. The overall experience was calm, well-organized, and deeply rewarding. For anyone seeking a trustworthy and experienced UK-based agency for Hajj or Umrah, this Umrah Tour…
I planned my Makkah Trip for Umrah with a UK-based travel agency, and the experience exceeded all expectations. From the very beginning, everything was handled with professionalism and care, making the entire journey seamless and stress-free. The ATOL-protected services provided complete peace of mind, and the team guided us clearly through every step of the visa process. Our stay in Makkah was exceptional. We were accommodated in a clean and luxurious 5-star hotel just minutes away from the Haram, which made performing Umrah extremely convenient and spiritually uplifting. The entire Makkah Trip was peaceful, well-organized, and truly rewarding. For anyone looking for a reliable and experienced UK-based agency for Hajj or Umrah, this is an excellent choice.